The Legislative Branch is Also Called Congress
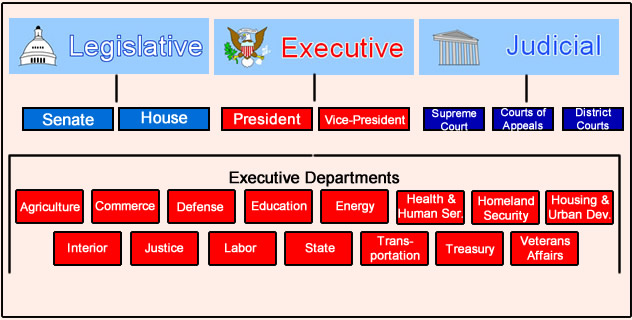
Congress is the legislative, or law-making body of the United States government. It is a bicameral entity, meaning that it consists of two houses, the Senate and House of Representatives. The Senate and House of Representatives each have specific powers, but the approval of both is necessary for the making of any law.
Powers of Congress
The U.S. Constitution gives Congress the power to levy and collect taxes, provide for common defense and promote the pursuit of liberty; to coin money and regulate its value; provide for punishment for counterfeiting; establish post offices and roads, promote progress of science, create courts under the Supreme Court, define and punish piracies and felonies, declare war, raise and support armies, provide and maintain a navy, make rules for the regulation of land and naval forces, provide for, arm, and discipline the militia, exercise exclusive legislation in the District of Columbia, and make laws necessary and proper to execute the powers of Congress.
Other Duties
Congress is also charged with oversight to monitor and review government programs, agencies, policies, and activities, prevent waste and fraud, protect civil rights and liberties, ensure executive compliance with law, gather information for making laws, educate the public, and evaluating executive performance.
United States Government Navigation