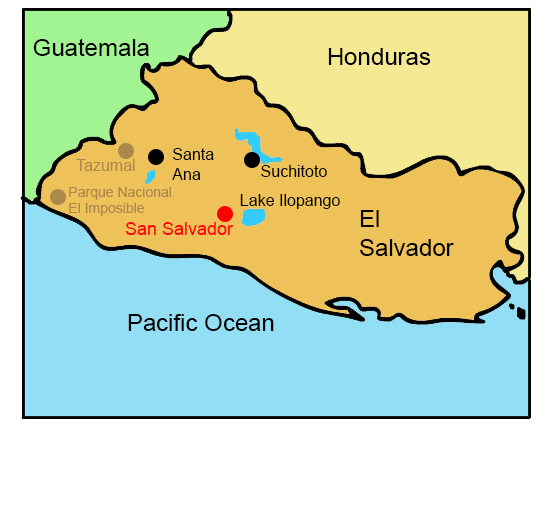
Click the points on the map to learn more.
 |
San SalvadorSan Salvador is both the capital and largest city in El Salvador. Between 1831-1838 the city was the capital of the Central American Federation, now it’s the center of trade and communication for El Salvador. The city was built on the volcanic slope near San Salvador volcano, which often results in damage from severe earthquakes. In 1986 and 2001, the city experienced intense earthquakes, killing thousands and damaging hundreds of thousands of buildings, structures, and homes. |
| Back to Map | |
 |
Santa AnaWith a population of 265,518, Santa Ana is the second largest city in El Salvador. It sits between mountains at an elevation of 2,182 feet. Santa Ana is the commercial center of western El Salvador. It also holds one of the world’s largest coffee mills, and is therefore a major coffee-processing center. |
| Back to Map | |
 |
Lake IlopangoLake Ilopango is the second largest lake in El Salvador. It sits in the crater of an extinct volcano, also called a caldera. In 1880 the water level rose, creating a volcanic island in the center of the lake now known as Ilopango Volcano. |
| Back to Map | |
 |
SuchitotoSuchitoto is considered the cultural capital of El Salvador. With a history that dates back a least 1,000 years, the village is famous for its cobblestone streets, lively festivals, and many resident artists. Suchitoto has become a popular tourist destination for its colonial buildings, scenic waterfalls, and exceptional birding. |
| Back to Map | |
 |
TazumalIn the K’iche’ language, Tazumal means “the place where the victims were burned”. The Tazumal ruins are the most important and extensively restored of the Maya ruins in El Salvador. They are part of the town of Chalchuapa, a large archaeological zone of ruins and important historical site in western El Salvador. |
| Back to Map | |
 |
Parque Nacional el ImposibleEl Imposible National Park is considered the most important natural area in El Salvador. The park gets its name from its dangerous gorge, which was said to claim many lives of farmers and pack mules transporting coffee from the region to the nation's Pacific ports. The park contains part of a coastal mountain range, including a dry tropical forest. The mountain range includes the steep “Impossible Pass,” from which the park gets its name. More than 500 species of birds live in the park. |
| Population: | 6,340,000 |
| Area: | 8,124 square miles |
| Capital City: | San Salvador |
| Largest City: | San Salvador |
| Currency: | U.S. Dollar |
| Official Language: | Spanish |
| GDP (Gross Domestic Product) | $24.26 billion |
- El Salvador is the only country in Central America that does not touch the Caribbean Sea
- El Salvador is known as the Land of Volcanoes
- El Salvador is the smallest country in Central America
- The main foods in El Salvador are rice, beans, and tortillas
- El Salvador has a tropical climate with two seasons: Rainy and dry
- At least 20% of El Salvador’s population lives abroad (in other parts of the world).
- El Salvador is the most densely populated country in Central America, and has a larger population than Nicaragua, Central America's largest nation by area.
- Coffee, sugar, rice, shrimp, and beef are the main agricultural products of El Salvador
- El Salvador gained independence from the Central American Federation in 1839
- From 1980-1992, El Salvador suffered through a violent Civil War caused by economic inequality.
|
|
 |
|
The blue stripes symbolize the Pacific Ocean and Caribbean Sea, and the white stripe symbolizes peace. El Salvador’s coat of arms includes a triangle representing equality and the three branches of government, with symbols of liberty, peace, and the people. Five volcanoes represent the five former members of the federation. The flag also includes El Salvador’s national motto of ‘God, Union and Liberty,’ and fourteen clusters of leaves representing the 14 states of El Salvador. |
|