The Parthenon was a temple built for Athena, the Greek Goddess of wisdom, civilization, and war, in the 5th century B.C. Located on the acropolis (hill) of Athens, the Parthenon is considered the most famous surviving building of ancient Greek architecture.
Although the Parthenon was originally a Greek temple, it was used as a treasury, Christian church, and mosque over the next thousand or so years. In 1687, the building was severely damaged after it was attacked by the Venetian military. In 1801, the British Earl of Elgin received permission to remove original marble sculptures from within the crumbling Parthenon. Today, those sculptures, known as Elgin Marbles, are housed in the British Museum. Other original sculptures from the Parthenon are housed at The Louvre in Paris. In 1975, the Greek government undertook a massive restoration project for The Parthenon and other ancient Greek structures. The project continues to this day.
Olympia
Olympia is a sanctuary in Greece where the first Olympic Games in world history were held. Starting sometime around 776 B.C., the Olympic Games were held every four years until they were abolished in 435 AD. The games were much different in ancient times than they are today. They held important religious significance and were punctuated by ceremonies and sacrifices to the Greek Gods. In the 6th century B.C., the mythical wrestler Milo of Croton became the first (and only) person to be victorious in six different Olympics.
In addition to the historical significance of the games, many important structures are situated around the sanctuary such as the giant gold and ivory Statue of Zeus (one of the Seven Wonders of the World), the Temple of Hera (the wife of Zeus), and the Hippodrome, an ancient Greek horse racing track. |
| |
Oracle at Delphi |
| |
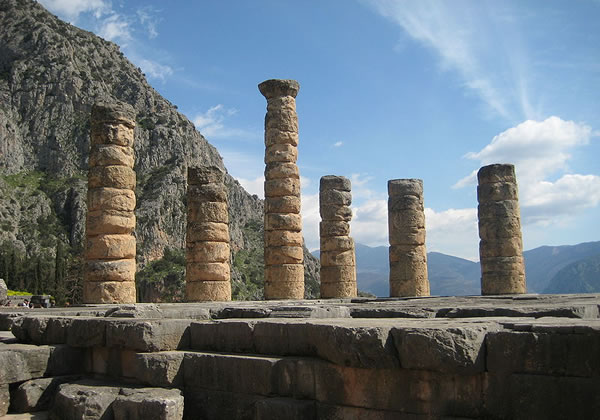

"Columns of the Temple of Apollo at Delphi, Greece" by Patar knight - Own work. Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 via Wikimedia Commons. |
| |
The Oracle at Delphi, an ancient temple to the Greek God of medicine, disease, and truth, Apollo, was the most important temple in ancient Greece. To the ancient Greeks, the Oracle at Delphi was the omphalos, or, center of the universe. Many historians believe the temple was originally built sometime around 1400 B.C.
People from throughout Greece would come to the temple to have questions about their futures answered by the Pythia - the priestess of Apollo. The Pythia was extremely influential and would be consulted before any major war, battle, or military decision was made. Before long, Delphi would become fabulously wealthy, as people throughout Greece would send art, gold, treasures, and riches to keep the Oracle on their side. |
| |
Delos |
| |
The island of Delos, located within the archipelago known as The Cyclades, is best known as the mythical birthplace of the Greek Gods Apollo and Artemis. Delos was an extremely important place in Ancient Greece and served as the main treasury for the Delian League, a confederation of Greek city-states under the leadership of Athens. Formed in 478 B.C., the Delian League's major purpose was to wage war against the Persians and various bands of pirates in the Aegean Sea.
In 1990, the island of Delos was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site. It is currently uninhabited and only used as an archaelogical site and for tourism. |
|
|