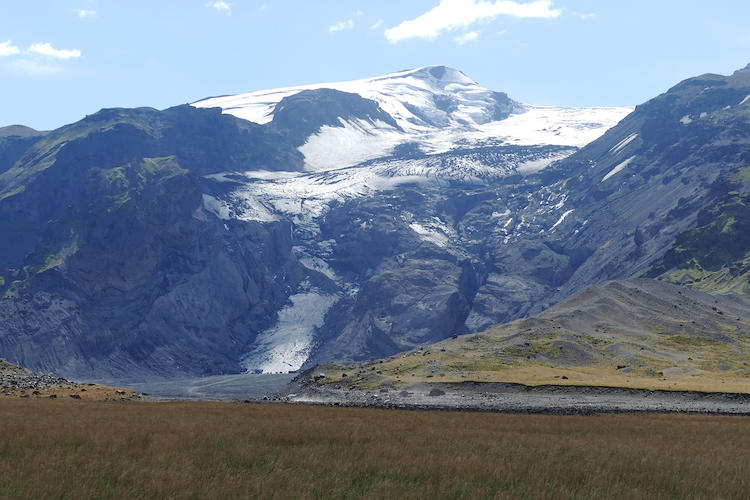
Eyjafjallajökull

Mt. Vesuvius
Image Credit - https://pixabay.com/users/yorick77-2006390/
Located in the heart of Iceland, the stratovolcano Eyjafjallajökull has etched its name into history, not only for its awe-inspiring geological features but also for a series of events that unfolded in 2010, capturing the world's attention.
Geological Features
Eyjafjallajökull, pronounced "ay-yah-fyat-lah-yoh-kootl," is a composite volcano crowned by an ice cap, making it a stratovolcano with distinctive features. Rising to 1,666 meters (5,466 feet) above sea level, Eyjafjallajökull is characterized by its steep slopes, rugged terrain, and the presence of glacial ice that blankets its summit.
The name "Eyjafjallajökull" translates to "Island Mountain Glacier," reflecting the volcano's location near the southern coast of Iceland and its ice-capped peak. The volcano is part of the larger volcanic system in the region, which includes neighboring Katla, a larger and more powerful volcano.
The Eruption of 2010
The eruption of Eyjafjallajökull in 2010 disrupted air travel and showcasing the powerful and unpredictable nature of volcanic activity. The eruption began in March 2010, with increasing seismic activity leading up to the explosive event that followed.
The eruption was characterized by the interaction of magma with glacial ice, leading to the production of fine ash particles and volcanic gases. The ash cloud, rich in silica and other abrasive particles, was propelled high into the atmosphere, posing a serious threat to aviation.
Global Impact on Aviation
The 2010 Eyjafjallajökull eruption had far-reaching consequences on global aviation. The volcanic ash cloud, drifting eastward over Europe, led to the closure of airspace across much of the continent. The microscopic ash particles can damage aircraft engines, posing a significant risk to flight safety.
The disruption resulted in the cancellation of thousands of flights, affecting millions of passengers and causing substantial economic losses for the airline industry. The event underscored the vulnerability of modern air travel to natural disasters and highlighted the need for improved monitoring and risk mitigation strategies.
Environmental and Local Impact
While the eruption wreaked havoc on air travel, it also had environmental and local consequences. The ashfall affected nearby communities, agriculture, and livestock. The fine volcanic ash, when deposited on the ground, can have both positive and negative effects on soil fertility, depending on the composition and amount.
In the long term, the eruption influenced the local landscape, creating new features and altering the topography of Eyjafjallajökull. The area around the volcano has become a subject of scientific study, providing insights into the recovery and resilience of ecosystems following volcanic events.
Post-Eruption Tourism and Scientific Research
In the aftermath of the eruption, Eyjafjallajökull became a focal point for scientific research and attracted tourists eager to witness the volcanic aftermath. Guided tours offer visitors the opportunity to explore the surrounding landscapes, witness the volcanic features, and learn about the ongoing research efforts.
The resilient ecosystem surrounding Eyjafjallajökull, coupled with the breathtaking scenery, has made the area a popular destination for nature enthusiasts and those interested in the dynamic geological processes at play in Iceland.
World Volcanoes